
Option trading
Trading options can give your portfolio extra flexibility, enabling you to trade in flat or volatile market conditions. You can use them to target profits or reduce your risk – making them key to many advanced strategies.
Open a CFD trading account to trade our full range of quarterly, monthly or daily options.
-
Access competitive options pricing
-
Trade options on 40+ markets across FX, indices and commodities
-
Manage your risk and offset your margin
Options with FOREX.com
-
1000s of strikesWith the options ladder in the FOREX.com platform, you can easily choose between a huge range of strike prices on your chosen markets.
-
Trade in any conditionsAre the markets trending, rangebound or flat? With options, you can find strategies for any market condition.
-
Trade options with CFDsWith FOREX.com, you’ll be trading option CFDs, so you can buy and sell options alongside our full range of markets.
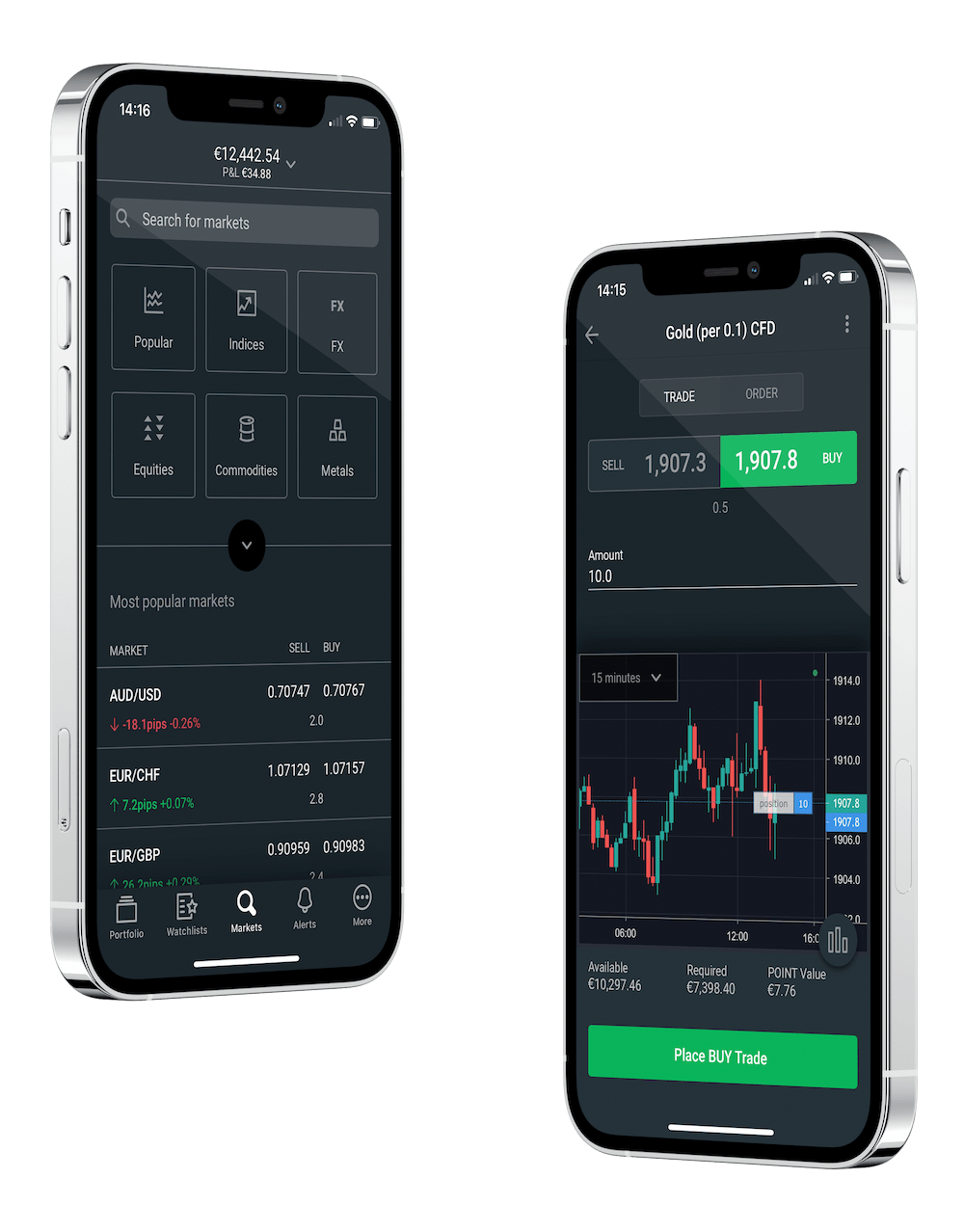
Award-winning mobile apps
Designed for instant control wherever you are, enjoy one-tap trading, intelligent market tools and a customisable layout to suit your trading style.
TradingView Charts
80 indicators, 11 chart types and 14 timeframes.
Trading Central
A research portal that uses technical analysis to scan the markets.
Performance Analytics
Analyse your decision making with the latest behavioural science technology.
What is option trading?
Option trading is the buying and selling of options contracts. These financial derivatives give you the right to trade their underlying market at a specific set price. You pay a premium for this right – and if you don't want to trade the underlying, you can leave the option to expire and only lose the premium.
You can buy options contracts to hedge your risk on an open position or sell them to unlock some advanced options strategies. They can be a powerful trading tool.
To see our full range of options, open a FOREX.com demo trading account. Or follow the link below to trade with real funds.

Latest options research
Options news and analysis
Options FAQ
What is the difference between calls and puts?
In options trading, calls and puts are the two different types of options contracts you can trade:
- Call options give you the right to buy the underlying market at the strike price before the option expires, giving the holder a long position
- Put options give you the right to sell the underlying market at the strike price before the option expires, giving the holder a short position
Are options good for beginners?
Options can be a useful market to get to know, but they are generally considered better suited to advanced traders. Why? Because there are a lot of factors that can impact their price movements – and because option sellers can end up taking on a lot of risk.
If you're a beginner trader, you might want to consider indices, FX or shares instead.
How can I start trading options?
You can start trading options by opening a FOREX.com account. You'll get access to our full range of quarterly, monthly or weekly option CFDs, alongside thousands of other markets.
Or if you're not ready for live trading, you can test out options with virtual funds by opening a free FOREX.com demo account.
What are options trading strategies?
Options traders can unlock some powerful advanced strategies by buying and selling calls and puts. However, some of these strategies are recommended for experienced traders only, as they may involve taking on high levels of risk.
In a straddle, for example, you buy a call and put on the same market with identical strike prices and expiries. Then, if the market moves significantly in either direction, one of your options will earn a profit. If the market remains flat, though, you'll lose the premium on both options.
How does options trading work?
Options trading works using contracts which give the holder the right to trade an underlying market at a set price – called the strike price. Call options give the holder the right to buy the market, while put options give them the right to sell it.
If the underlying market moves beyond the strike price, the holder can exercise their option for a profit. If not, they lose the premium and the seller makes a profit.

