
Over the course of the past two decades, the forex market has grown into the world’s largest financial venue. In fact, according to the Bank of International Settlements (BIS) Triennial Survey for 2019, the forex market regularly posts an average daily turnover of more than $5.0 trillion. While these averages are down from the $6.0 trillion of 2014, the forex remains a preeminent global marketplace.
Given its immense size and breadth, forex volatility can spike because of a multitude of reasons. The leading market drivers are classified into two distinct groups: economic and geopolitical factors. Given the importance of these factors, understanding how global events can affect the foreign exchange market is a key aspect of successful trading
Global Events & The Foreign Exchange Market
When it comes to market-moving events, elections frequently top the list. Whether referencing the Brexit Referendum of 2016 or leadership contests in the US, UK, or Japan, the impact on the world market after an election can be substantial. For example, in the wake of the UK’s shocking decision to depart the European Union in June 2016, GBP/USD moved a staggering 1800 pips in a single day, 50% more than its range over the previous six months.
In addition to geopolitical events such as elections, routine economic indicators such as GDP and trade balance can greatly influence a nation’s exchange rate. If you’re interested in becoming a successful currency trader, then taking the time to learn how global events can affect the foreign exchange market is a necessity.
Key Economic Factors
For individuals interested in successfully trading currencies, it’s imperative to stay abreast of important economic events as they unfold. One of the best ways to accomplish this goal is through referencing an economic calendar. The daily calendar lists the key events and times for each release, making it easy for the active forex trader to keep track of all pertinent information.
The following is a breakdown of several key economic metrics that impact the forex market:
Central banking policy
When it comes to leading forex market drivers, monetary policy is perhaps the most important. Monetary policy is a multifaceted approach to promoting pricing stability through managing a nation’s money supply. Monetary policy is carried out by a country’s central banking authority via open market operations, interest rate adjustments, and satisfying reserve requirements. Examples of the world’s leading central banks include the Bank of England (BoE), Bank of Japan (BoJ), the United States Federal Reserve (Fed), and the European Central Bank (ECB). Generally speaking, an unexpected interest rate increase benefits the underlying currency, while a surprising rate cut tends to lead to weakness in the currency in question.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
A country’s GDP is a representation of economic activity, aggregate output, and growth. Essentially, higher GDP figures represent more economic output, while lower values suggest less activity. According to a 2020 study from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the United States (US$20.49 trillion), China (US$13.4 trillion), and Japan (US$4.97 trillion) are the three global leaders in GDP. While critical for assessing the overall health and power of a nation, GDP figures may not lead to dramatic market moves as the data is typically released more than a month (and often two or three months) after the relevant time period.
Unemployment rate
A country’s unemployment rate is a representation of unemployed persons relative to the labor force. High unemployment rates typically accompany recessionary cycles and sluggish GDP growth, while low rates signal robust economic performance.
Inflation rate
Any study of how global events can affect the foreign exchange market isn’t complete until the concept of inflation is addressed. Inflation measures the rise in consumer and producer prices. Central banks primarily seek to manage inflation by raising interest rates, which can limit the impact of currency devaluation. Two key metrics used to place inflation into context are the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI).
Both inflation and unemployment are key areas of focus for central banks, so the ensuing market reaction is often viewed through that lens. In other words, higher-than-expected inflation and lower-than-anticipated unemployment figures suggest that the central bank may be more likely to raise interest rates, leading to strength in the underlying currency and vice versa.
By monitoring how the forex market reacts to surprises in these key economic releases and others, traders can develop strategies to take advantage of the ensuing volatility and trends.
Geopolitical Market Drivers
In contrast to most economic factors, geopolitical market drivers typically arise less frequently. 2020 has brought several of these events, ranging from the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic to the scheduled US presidential election. Each had a profound impact on forex trade through enhancing volatility. As the chart below shows, market movement tends to increase around significant events, especially when those events represent negative surprises:
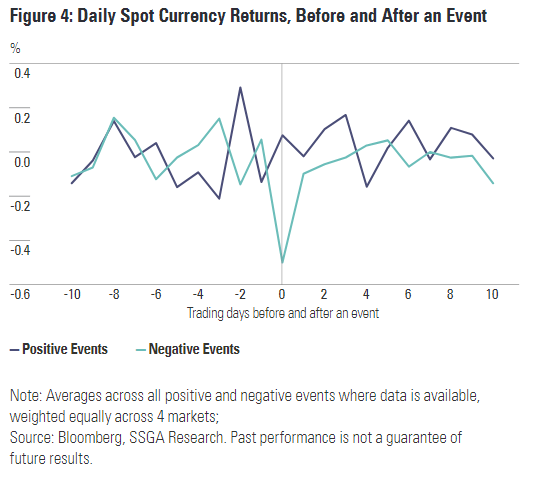
Source: State Street Global Advisors, Bloomberg
The following geopolitical factors are critical to forex price action. They all have the potential to drive forex valuations directionally, at the drop of a hat.
Political events
As a general rule, the forex market isn’t fond of political uncertainty. In fact, books have been written about the positive and negative impacts on the world market after an election cycle. As we noted above, the surprise passage of the 2016 Brexit Referendum placed extreme pressure on the British pound sterling (GBP). Amid the uncertainty, the pound fell to levels not seen since 1985. 2019 brought another example of election year volatility, with Argentina drastically restricting US dollar access to limit domestic currency market fallout.
Natural Disasters
Hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires rear their heads unexpectedly and can have severe financial consequences. As an illustration, the Australian brush fires of late-2019 and early-2020 had dramatic economic and currency market impacts. With damages estimated to measure in billions of Australian dollars, the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) quickly adopted a more supportive policy. Subsequently, a series of RBA rate cuts sent the Australian dollar significantly lower vs the US dollar, highlighting the interplay between economic and geopolitical events.
Humanitarian crises
Wars, terror attacks, and pandemics can have a devastating impact on the economies and currencies of affected nations. One of the premier examples of a global humanitarian crisis is the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic of 2020. Widespread quarantines, travel bans, and shutdowns quickly sent the world’s economy into a tailspin. Among the hardest hit currencies was the US dollar, which fell to multi-year lows following the FED’s implementation of aggressive quantitative easing (QE) policies and aggressive fiscal policy out of Washington.
Conclusion
In many ways, it’s difficult to overstate the importance of how global events can affect the foreign exchange market. From scheduled economic data releases to “Black Swans” such as COVID-19, the impact of such factors can be dramatic and widespread. To any aspiring forex trader, staying “in the know” regarding such events is a prerequisite for successful trading.
After putting the time into studying price action and analyzing market fundamentals, it’s time to trade. Designed for currency market participants of all sizes, Forex.com caters to spread, commission, and high-volume FX traders. For more information on selecting an account type that is right for you, get in touch with our team today!




