Commodities trading FAQs
Browse this FAQ section for more information about commodities trading.
- What commodities does FOREX.com offer?
- What are commodity CFDs?
- What is the cost of commodity CFD trading?
- What is the commodity CFD nightly finance charge and how is it calculated?
- When do commodity CFD orders expire?
- How are Non-Expiring Commodities (NEC) priced?
- What is the margin for commodities trading?
- How do I calculate how much margin I need to trade a commodity?
- What market changes may affect Oil trades?
What commodities does FOREX.com offer?
With FOREX.com, you can trade crude oil, natural gas, corn and more as CFDs. Click here to view our range of markets.
What are commodity CFDs?
A CFD, or contract for difference, is an agreement to exchange the difference between the opening and closing price of the position under contract, rather than buying and selling the underlying security outright.
What is the cost of commodity CFD trading?
FOREX.com is compensated by the spread, which is the difference between the bid and ask prices. View our live spreads.
In addition, you may be charged a nightly finance charge if you hold a position overnight, after 5pm ET.
What is the commodity CFD nightly finance charge and how is it calculated?
With most CFDs, financing is debited for long positions or credited for short positions daily if you are in a position at 5pm ET.
These charges are typically calculated as follows:
F=(S x P x R)/D
F - Daily Financing Charge
S - Number of CFDs (2500)
P - Closing Price
R - Relevant interest rate benchmark, +250 basis points for long positions or -250 basis points for short positions, e.g. (4.50% + 3.00%) = 7.50%
D - Number of days, i.e. 365 for UK stocks and 360 for all others
When do commodity CFD orders expire?
FOREX.com offers two types of CFDs: futures CFDs, which are dated for a specific contract month and expire, and cash CFDs, which are non-expiring and roll into the next contract month, with a basis adjustment (credit or debit in the difference between contract months). Note that only the futures CFDs are available on the MetaTrader 4 platform. You can check standard expiry definitions here. This can also be found under the Market 360 tab for each market on the FOREX.com Web Trading platform, or under the Company tab in the Terminal window of MetaTrader 4.
When a CFD futures market expires, we close all open positions based on our most recent prices and all open orders are cancelled. To retain your open positions in a market, you must manually open a new position in the next contract month.
How are Non-Expiring Commodities (NEC) priced?
To price these non-expiring markets, we use two sufficiently liquid futures contracts on the underlying commodity. This is usually the two with the nearest expiry date.
The contract with the closest expiry date is called the Front month contract and the second-nearest expiry date is called the Far month contract.
Throughout the duration of the Front month contract, the price of the NEC will gradually move from the price of the front month to the price of the far month.
As there will be an adjustment to the NEC Market price every day, your account will be subject to an adjustment in the form of a Credit/Debit to offset this price adjustment. For example, if the NEC contract is adjusted by +2 points, clients with long positions will be debited 2 x stake and clients with short positions will be credited 2 x stake. See further explanation and video below.
In our video, the front month is labelled ‘A’ and the far month ‘B’.
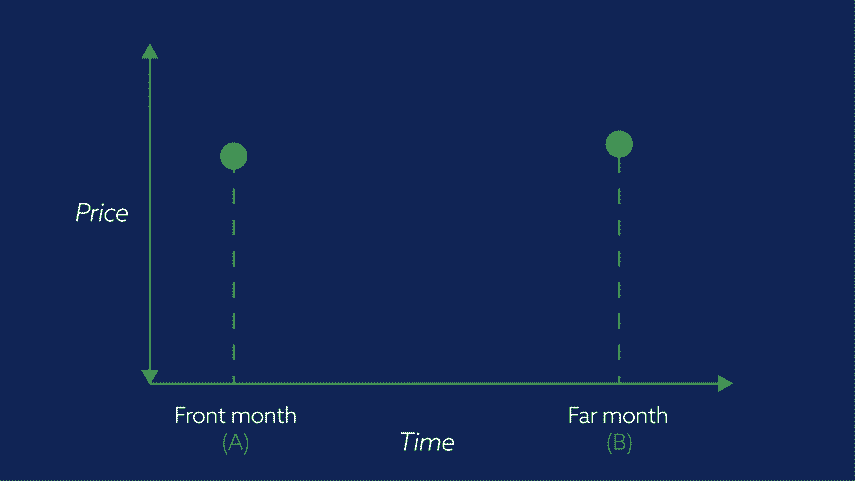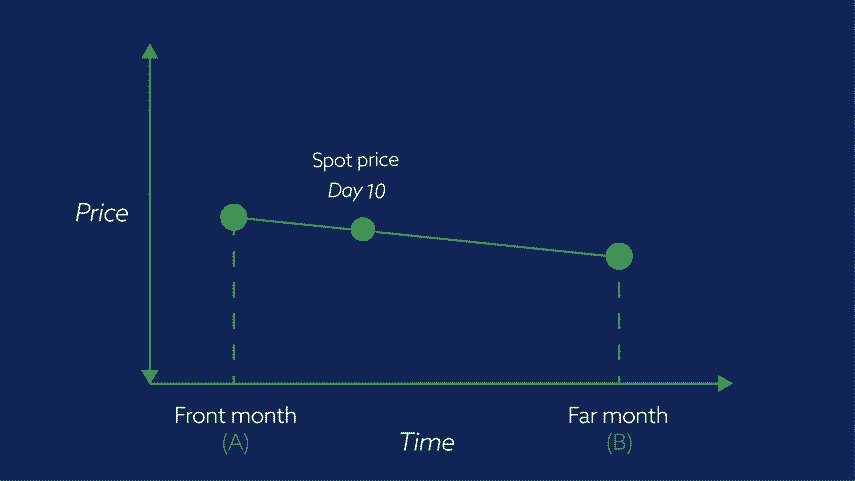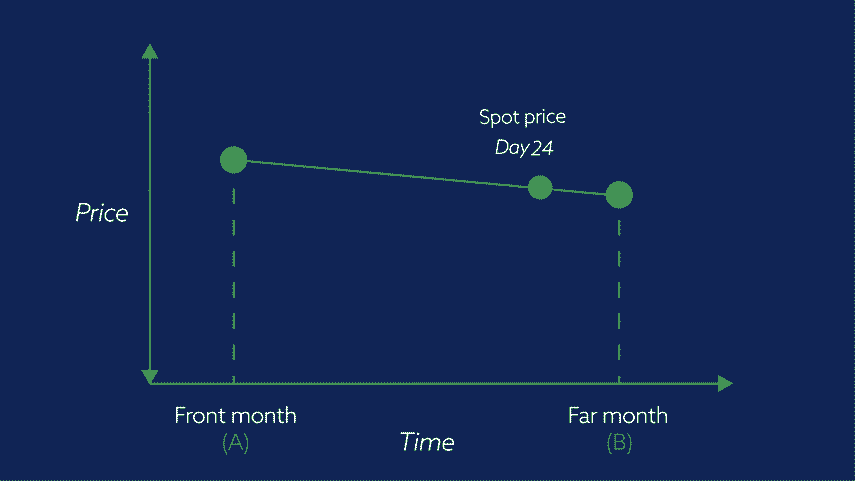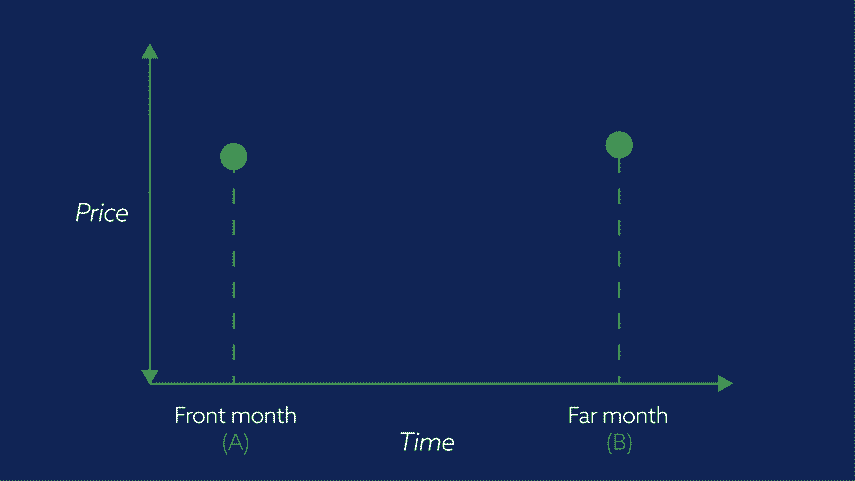
NEC contract market prices move from the price of market ‘A’ towards the price of market ‘B’ as the expiry date of ‘A’ becomes closer. The price of market ‘B’ may be higher or lower, depending on the commodity, than that of market ‘A’.
Daily adjustments for NEC contract markets reflect a day’s movement from ‘A’ towards ‘B’.
What is the margin for commodities trading?
Margins for commodities vary according to the market and type of account.
For more information on a specific market, please check the Key Market Information or Market 360 within the trading platform, or explore our margin requirements page.
How do I calculate how much margin I need to trade a commodity?
The formula to calculate how much margin is required is quantity x price x margin.
What market changes may affect Oil trades?
Changes Affecting Oil Trades:
|
Scenario |
Change |
|
Oil price drops below $5.00 |
In the event the price of any of our oil contracts drops below $5.00/barrel, trading restrictions may then apply as follows: - Not allowing any new opening orders or trades, which includes resting orders to open. Pending orders would remain on the clients account and become executable when the price is back above $5.00 and stabilizes. - Existing open (long and short) positions switching to close-only, with no ability to add to the position until the price is back above $5.00 and stabilizes. Note: FOREX.com will determine at its sole discretion when it believes the market has stabilized and when to re-open the market, allowing the ability for clients to initiate new position(s) and/or add to existing position(s). |
|
Oil price reaches zero |
In the event the price of any our oil contracts reaches or falls below zero, we will close any long or short positions on that market at the current available market price. Please note that the underlying price could be negative at the time of closing, and if such, we reserve the right to adjust the trading account accordingly. |
Markets affected:
|
Platform |
Market(s) |
|
Web Trader |
US Crude Oil (all contracts) UK Crude Oil (all contracts) |
|
MT4 |
WTI/USD Brent/USD |
|
MT5 |
US Crude Oil (all contracts) UK Crude Oil (all contracts) |